California Academy of Sciences and Presidio Trust repopulate sand dunes with relative of extinct Xerces Blue butterfly.
Four years in the making, the historic reintroduction was made possible by a multi-organization effort to restore the Presidio’s native dunes and identify the Xerces Blue’s closest living relative
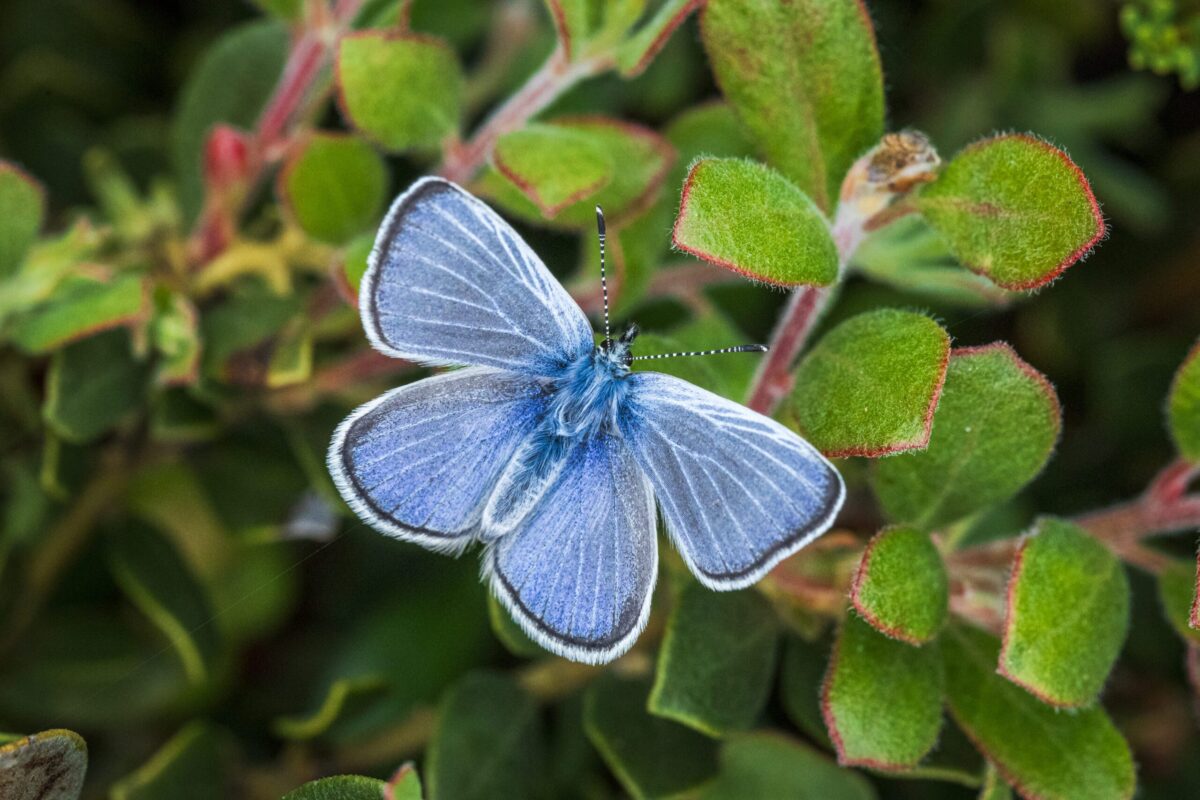
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (April 15, 2024) — In a historic reintroduction that further restores native ecosystems in San Francisco, the California Academy of Sciences and Presidio Trust released Silvery Blue butterflies (Glaucopsyche lygdamus)—the closest living relative of the extinct Xerces Blue butterfly (G. xerces)—last week in the sand dunes of the Presidio, a national park site.
The butterfly’s successful release in San Francisco was made possible by the restoration of more than 50 acres of the Presidio’s dune habitat and the identification of a compatible “surrogate” species that will revive an ecosystem function lost with the human-driven extinction of the Xerces Blue. Funding for two critical stages of the project, initial gene sequencing and early fieldwork, was provided by the conservation organization Revive & Restore.
“This isn’t a Jurassic Park-style de-extinction project, but it will have a major impact. The Silvery Blue will act as an ecological ‘stand-in’ for the Xerces Blue, performing the same ecosystem functions as both a pollinator and a critical member of the food web,” says Durrell Kapan, PhD, a senior research fellow and the lead Academy researcher on the project. “To ensure a successful reintroduction, we needed to identify a subpopulation that shared genetic and ecological similarities with the Xerces Blue: a sand dune specialist that is well-adapted to the cool, foggy climate of San Francisco and relies on the same host plant, deerweed (Acmispon glaber).”
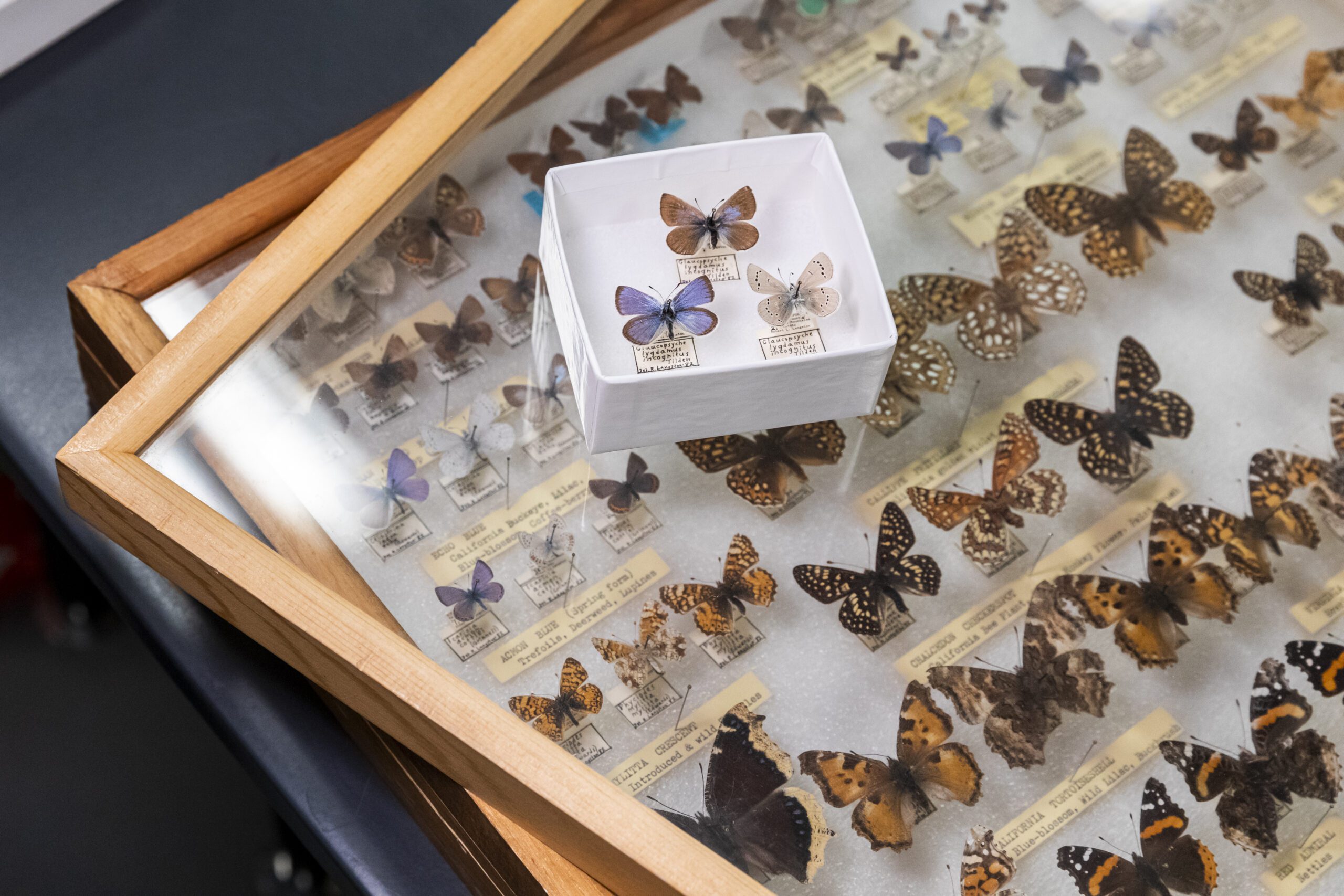

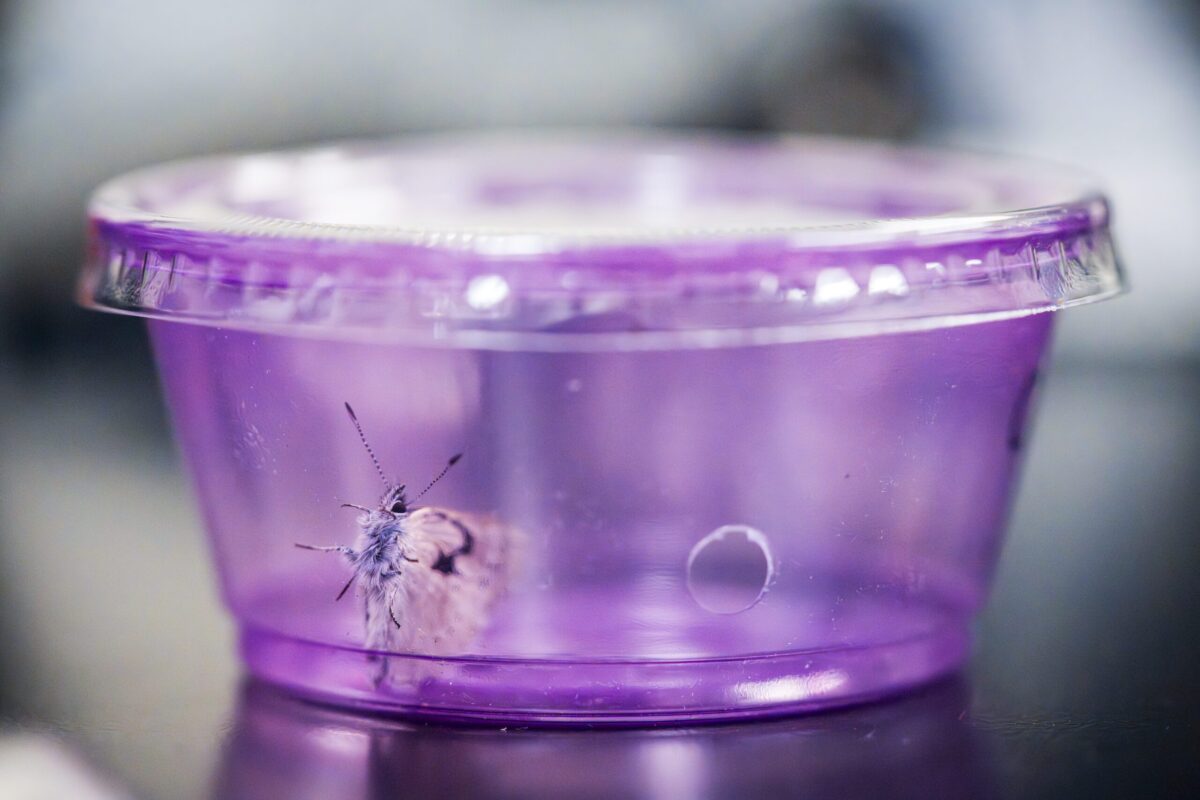
Specimens of the extinct Xerces Blue butterfly, some dating back more than a century, are housed in the Academy’s scientific collections. © Gayle Laird
Learning from our past
The Xerces Blue was the first butterfly species in the United States to be driven to extinction from habitat loss caused by human development. Its entire population was confined to sand dunes that extended from the Presidio through Ocean Beach to Fort Funston in what is now San Francisco’s Richmond and Sunset neighborhoods. Though the species went extinct more than 80 years ago, the iconic butterfly—whose name inspired the Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation—serves as a reminder of the importance of protecting invertebrates and their habitats.
“The loss of even a single species can have ripple effects across local ecosystems,” says Phoebe Parker-Shames, PhD, Presidio Trust wildlife ecologist. “Enhancing biodiversity is critical to healthy, functioning ecosystems and the people that rely on them, so that we are more resilient to climate change, invasive species, and other negative human impacts.”
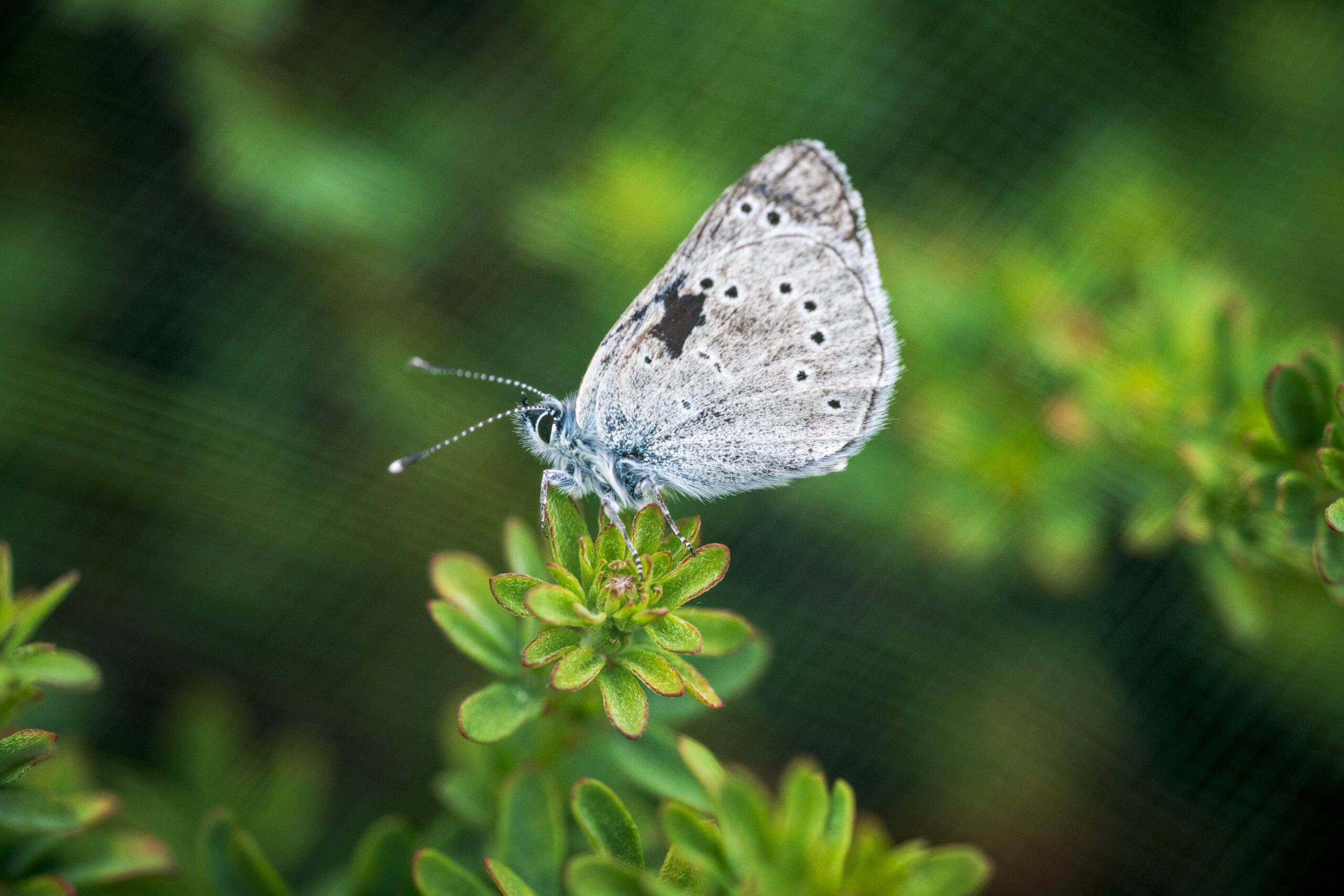

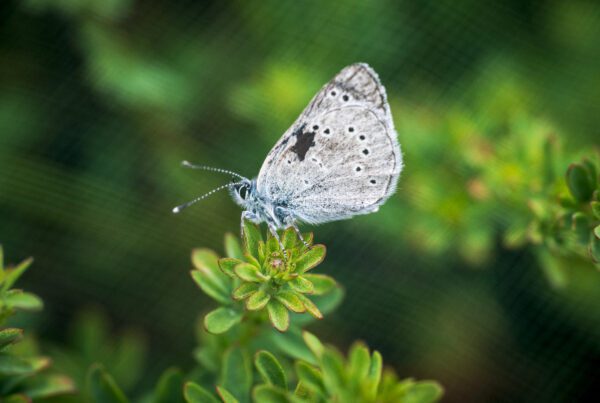
Silvery Blue butterfly (Glaucopsyche lygdamus), the closest living relative of the extinct Xerces Blue butterfly (G. xerces) | © Gayle Laird
Finding an ecological stand-in for the Xerces Blue
To fill the gap that the Xerces Blue left behind when it disappeared in 1943, researchers first tapped into the California Academy of Sciences’ invaluable collection of nearly 46 million scientific specimens. Utilizing the Academy’s in-house genetic sequencing capabilities, scientists analyzed Xerces Blue specimens—some dating back more than a century—to better understand its genome. Three years of niche modeling and fieldwork confirmed researchers’ prediction that a group of Silvery Blues about 100 miles south of San Francisco could successfully fill the ecological niche left by the Xerces Blue. “We were excited to find thriving populations of Silvery Blues from the sandy coastal scrub habitat at foggy sites in Monterey County that we predict are the best candidates for translocation to the Presidio,” Kapan says.
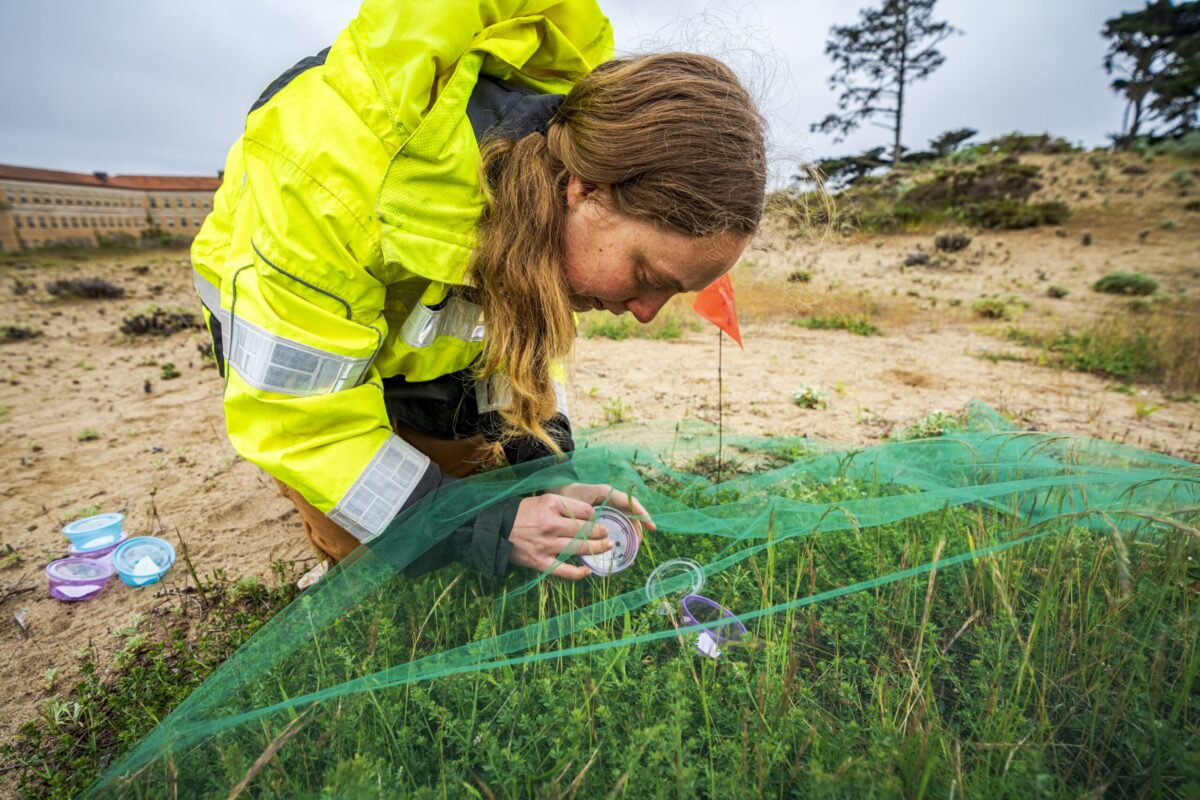
With a healthy dune habitat and plenty of deerweed to support the Silvery Blues in the Presidio, researchers from the Academy and Creekside Science secured permission to gather butterflies from UCSC’s Fort Ord Natural Reserve and Garrapata State Park in Monterey County and transport them to San Francisco. Each butterfly enjoyed a few drops of fruit punch-flavored Gatorade to sustain them on the drive—a tried-and-true method for butterfly translocation—and was marked for future identification.
The team will continue to track their movements using high-resolution photographs to identify their markings, similar to identifying individual whales by their flukes. “Our hope is that these new residents will lay their eggs and return in even higher numbers next spring,” says Lew Stringer, associate director of natural resources at the Presidio Trust.
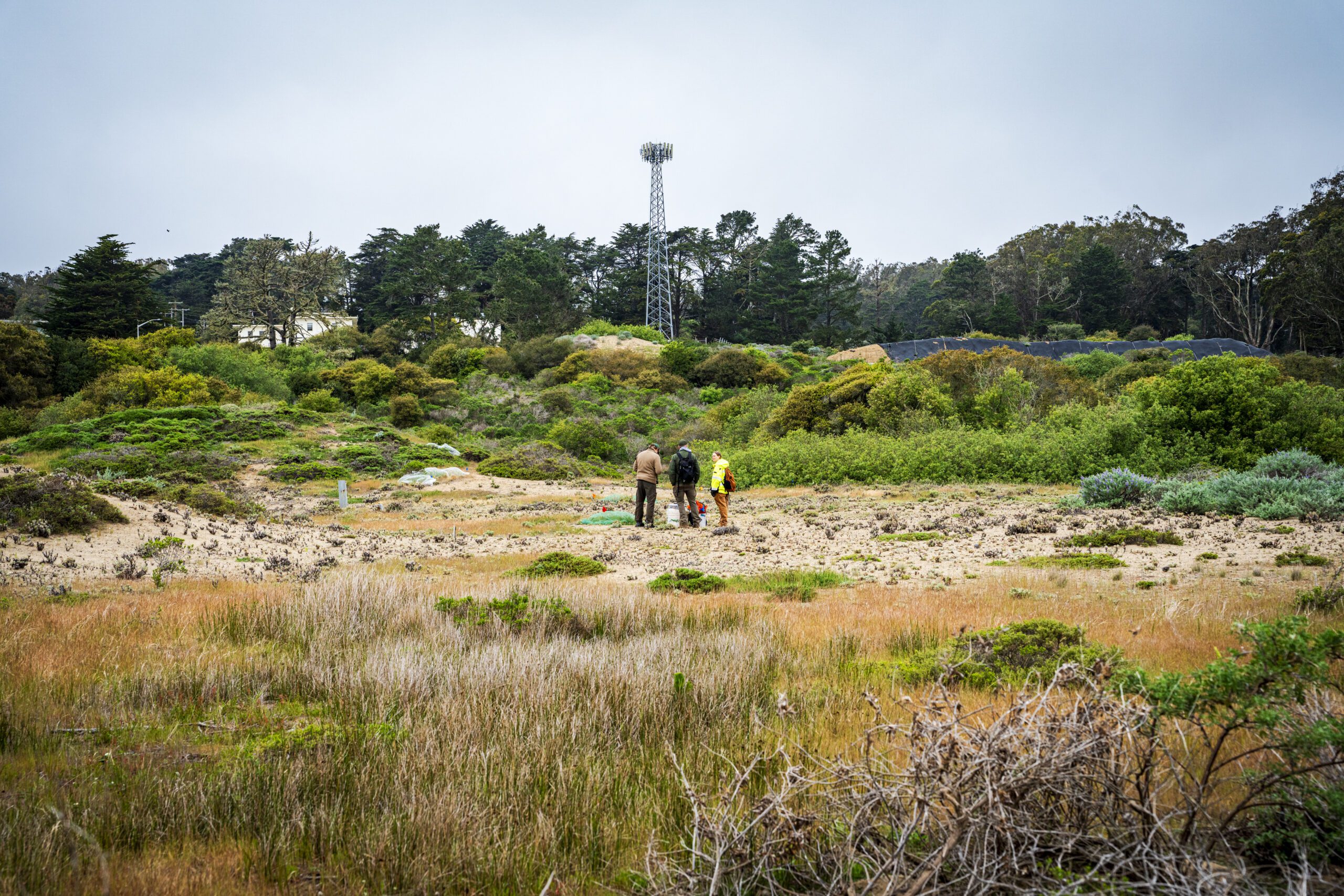

The butterfly’s successful release in San Francisco was made possible by the restoration of more than 50 acres of the Presidio’s dune habitat | © Gayle Laird
Restoring the Presidio sand dunes
“We are so pleased that 30 years of habitat restoration in the Presidio has recreated the natural conditions necessary to support the Silvery Blues,” says Jean Fraser, CEO of the Presidio Trust. “Stewarding the natural resources of the park is one of our primary values, and it’s great to see indications that the ecosystem is increasingly healthy and more resilient. This return is another example of how humans and wildlife don’t just co-exist, we thrive together in the Presidio.”
For over three decades, the Presidio Trust and the Golden Gate National Recreation Area have worked to ecologically restore the former military base and increase overall biodiversity. Park stewards have facilitated the return of native and endangered plants and have successfully reintroduced several endemic species to the Presidio, from rough-skinned newts (Taricha granulosa) and western pond turtles (Actinemys marmorata) to the San Francisco forktail damselfly (Ischnura gemina) and the variable checkerspot butterfly (Euphydryas chalcedona). Now teeming with life, the Presidio is a known biodiversity hotspot in San Francisco.
Regeneration through partnership
The four-year project involved a collaborative team of scientists and park stewards from the Academy, Presidio Trust, Creekside Science, Golden Gate National Recreation Area, and Revive & Restore. Funding for two critical stages of the project, initial gene sequencing and early fieldwork and later ecological niche modeling and butterfly translocations, was provided by Revive & Restore and the McGuire Center for Lepidoptera and Biodiversity at the Florida Museum of Natural History respectively. The Academy, Presidio Trust, and Golden Gate National Recreation Area are also part of Reimagining San Francisco, an urban nature alliance of more than 40 organizations that aims to increase biodiversity and equitable access to nature throughout the city.
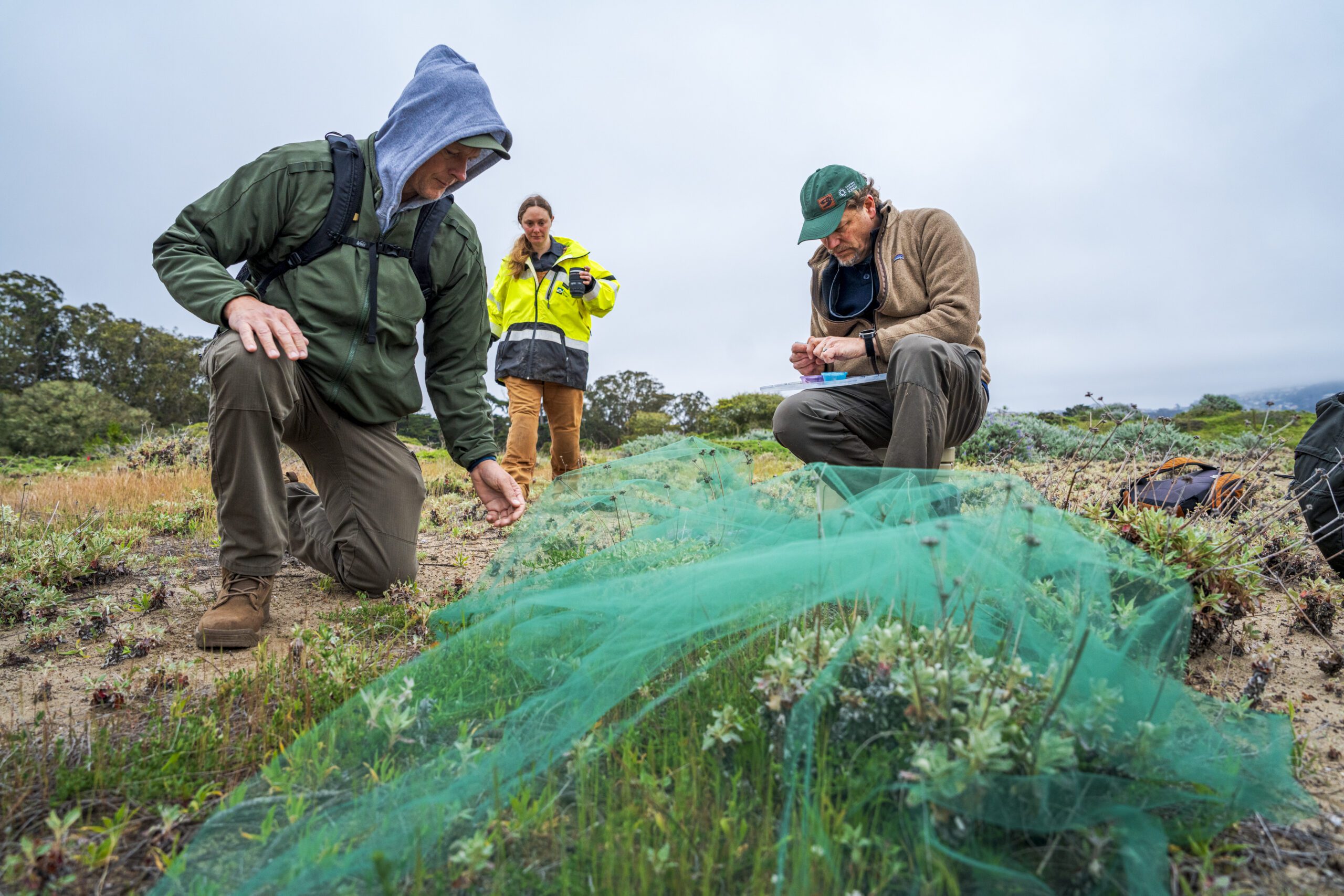

Researchers place Silvery Blue butterflies under netting to prevent them from flying away | © Gayle Laird
About the California Academy of Sciences
The California Academy of Sciences is a renowned scientific and educational institution with a mission to regenerate the natural world through science, learning, and collaboration. Based in San Francisco’s Golden Gate Park, it is home to a world-class aquarium, planetarium, and natural history museum, as well as innovative programs in scientific research and environmental education—all under one living roof. Museum hours are 9:30 am – 5:00 pm Monday – Saturday, and 11:00 am – 5:00 pm on Sunday. Admission includes all exhibits, programs, and shows. For daily ticket prices, please visit www.calacademy.org or call (415) 379-8000 for more information.
About the Presidio and the Presidio Trust
The Presidio is one of America’s most visited national park sites, located within the Golden Gate National Recreation Area. Spanning 1,500 acres next to San Francisco’s Golden Gate Bridge, the Presidio is among the most biologically diverse parks in America. Historically a home to native peoples and a military post under three flags, its facilities have been reinvented as museums, restaurants, hotels, homes, and offices. The Presidio Trust is the federal agency that stewards the Presidio, in partnership with the National Park Service and with support from the Golden Gate National Parks Conservancy. The Trust sustains the Presidio by leasing homes and workplaces and offering visitor amenities.
About Revive & Restore
Revive & Restore is the leading wildlife conservation organization promoting the incorporation of biotechnologies into standard conservation practice. The Sausalito, California nonprofit was formed in 2012 with the idea that 21st century biotechnology can and should be used to enhance genetic diversity, build disease resistance, and facilitate adaptation. Our mission is to enhance biodiversity and restore ecosystems through the genetic rescue of endangered and extinct species. Learn more at www.reviverestore.org.
More posts in News & Media